|
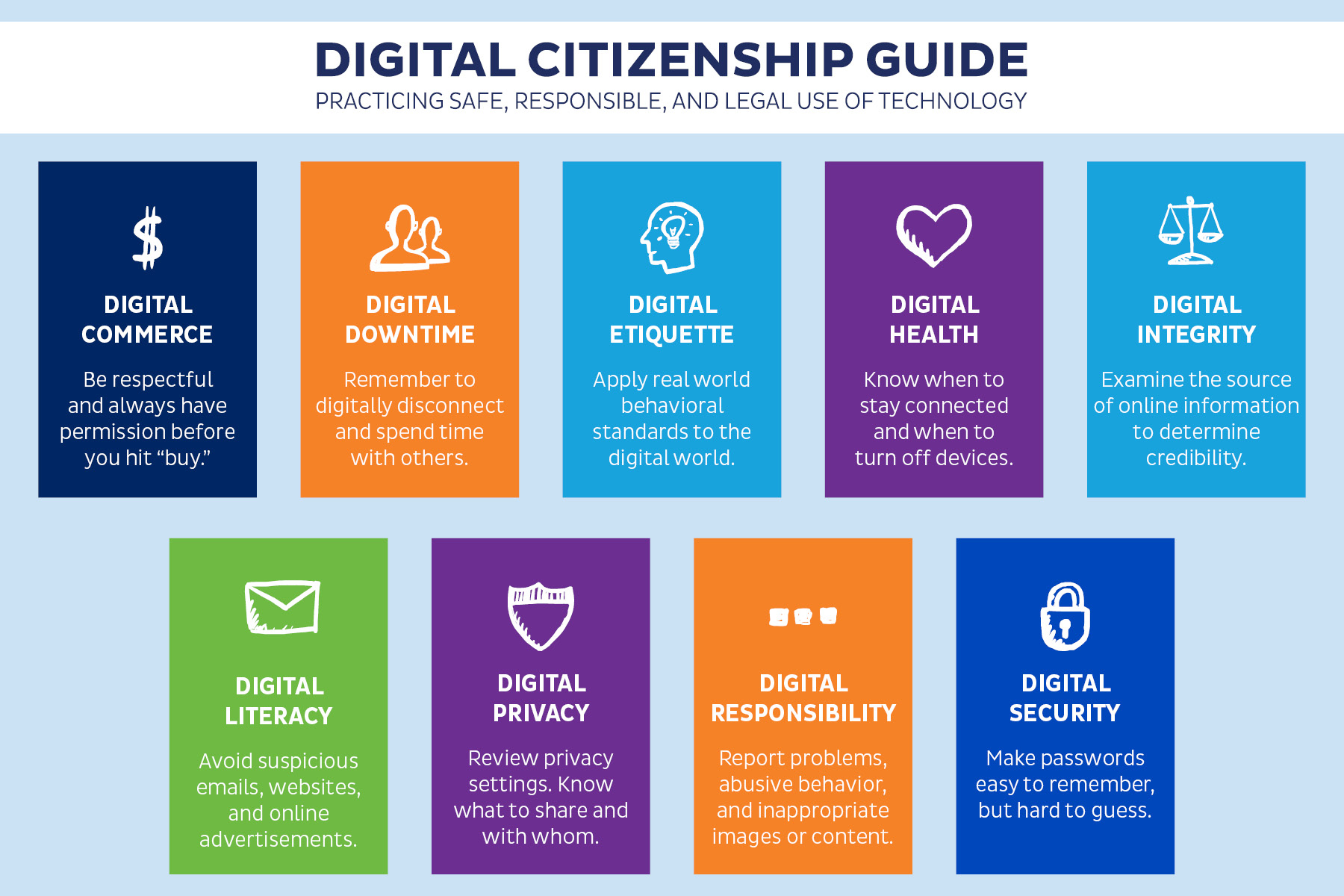
What is Digital Citizenship?
Digital citizenship refers to the responsible use of technology to learn, create and participate online. As a member of the University of Edinburgh community, it’s your social responsibility to be a good digital citizen, which means treating others with dignity and respect in both physical and virtual spaces. The following principles are a good place to start:
1. Use the Golden Rule
How we behave in virtual spaces shouldn’t differ from how we behave in physical spaces. It’s important to act with empathy, compassion, and kindness in both your online and offline interactions.
2. Respect differences
The University prides itself on fostering a truly international community, which means respecting cultural differences and honoring diverse perspectives. If you disagree with someone online, engage thoughtfully and avoid personal attacks.
3. Pause before posting
The internet is a place of knowledge exchange, but conversations can get heated. It’s worth pausing for a moment before responding to anything in anger. Avoid posting or sending anything that could hurt someone else, damage someone’s reputation or that of the University, or threaten either your own safety or the safety of others.
4. Stand up for yourself and others
If you ever feel unsafe online, tell someone. You can also support others who are targets of online abuse or cruelty by reporting activity that threatens a person's safety and preserving evidence of inappropriate or unsafe behavior.
|
Why is digital citizenship important?
The University of Edinburgh is an international community that prides itself on our commitment to equality, diversity, and inclusion. We have a duty to one another to build a community that works for everyone both online and off. The concept of digital citizenship underpins each of the four key themes in the University’s Strategy 2030.
People
The University’s Strategy 2030 states, “We will set an example for others by conducting ourselves with integrity, transparency, honesty and clarity at all times. We will always value and protect freedom of expression, while respecting the boundaries dictated by law, decency, ethics and respect for others.” The same applies to both physical and digital spaces.
Research
The ways in which we manage and store research data constitute an important digital safety and citizenship consideration. Being “critically aware of the ethical, legal and regulatory responsibilities of research,” as the Strategy 2030 states, means storing data safety and effectively.
Teaching and Learning
Creating a sense of digital citizenship is key to improving student satisfaction and wellbeing. In line with the University’s commitment to widening participation, we have a duty to offer accessible and responsive educational services that ensure students from any background feel safe and supported whether studying on campus or online.
Social and Civic Responsibility
Information security is a key part of the University’s social and civic responsibility. In order to “ensure that our actions and activities deliver positive change locally, regionally and globally,” we must start by creating an online community committed to making the internet a safer, more inclusive space.
Equality, Diversity and Inclusion Online
The University is fully committed to fostering safe and inclusive spaces both across campus and online. Unfortunately, the internet was not created with equality, diversity, and inclusion in mind, meaning we all have to make a conscious effort to promote these values and protect the most vulnerable members of our diverse and international community. Watch the video below, “Making the Internet a Safer Place” for an introduction to the concept of cyberhate and how you can do your part to make our online community safer for everyone.
|